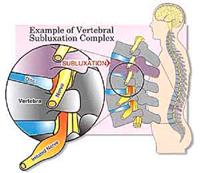
 Vertebral subluxation complex is the result of a neurological interference caused by bad biomechanics and bad spine alignment. This spinal disturbance provokes nerve irritation and prevents the nervous system signals from circulating adequately between the brain, the muscles and the body’s organs resulting in a neuromusculoskeletal imbalance.
Vertebral subluxation complex is the result of a neurological interference caused by bad biomechanics and bad spine alignment. This spinal disturbance provokes nerve irritation and prevents the nervous system signals from circulating adequately between the brain, the muscles and the body’s organs resulting in a neuromusculoskeletal imbalance.
To summarize, the vertebral subluxation complex causes an overall malfunction of the affected joint, which will possibly cause local pain, as well as a potential reduced function of certain structures (organs, muscles, tissues, etc.) serviced by the nerves in the affected area. The body’s general response is muscle contraction in order to try and stabilize the painful region.
The 5 principal aspects of vertebral subluxation
- Vertebral kinesiopathology: abnormal movement or poor vertebral alignment;
- Neuropathophysiology: abnormal nervous system function (nerve interference);
- Myopathology: abnormal muscle function;
- Histopathology: abnormal soft tissue function (discs, ligaments);
- Pathophysiology: Body degeneration (degenerative osteoarthritis).
 Possible causes of subluxation
Possible causes of subluxation
- Emotional, physical, chemical
- Sub-optimal work posture
- Repetitive movements
- Poor lifting habits
- Bad sleeping habits: sleeping on one’s stomach or with your arms above your head
- Unhealthy diet (chemical stress)
- Emotional stress
- Toxic environment: pollution, household products, cigarettes, etc.
- Physical traumas: automobile accidents, falls, operations, etc.
- Trauma during birth (for newborns or post-partum women)
